Long and Short Vowels in Korean Peer Reviewed Articles
- Original article
- Open Admission
- Published:
L1 Korean vocalic transfer in developed L2 Korean learners' production of Vietnamese monophthong vowels
Asian-Pacific Journal of Second and Foreign Linguistic communication Education volume 3, Article number:13 (2018) Cite this commodity
Abstract
This paper reports a study that investigated the function of prior native or offset language (L1) phonological and phonetic learning on the integration of vowel quality features in the production of second linguistic communication (L2) vowels by examining adult L2 Korean learners' product of Vietnamese monophthong vowels in an fake and a read aloud tasks. Three groups of participants took part in the report (eleven control Vietnamese, 11 Korean learners of Vietnamese, and 10 control Korean). The stimuli consisted of 9 Vietnamese monophthongs /i, e, ɛ, a, ɔ, o, u, ɤ, ɯ/ and 8 Standard Korean vowels / i, ɛ, east, a, o, u, ʌ, ɨ /. The results showed that Vietnamese vowels /ɛ/ and /eastward/ produced past Korean learners merged in vowel space, proving how a phonemic merger in L1 can influence speakers' perception and product of non-native vowels. Moreover, the 3 Vietnamese vowels /ɔ/, /o/ and/ ɤ/ produced past Korean learners in both tasks tend to cluster together. In general, the findings of this study showed that Korean learners transfer their L1 vowel quality features into the production of Vietnamese vowels.
Introduction
2nd-linguistic communication learners typically accept a wide range of difficulties with the phonetic and phonological systems of the second language (L2). When non-native speakers learn a 2d language, they have often shown difficulties in perceiving and producing contrastive L2 sounds which do not be in their native linguistic communication (L1) arrangement. Some research results showed that the failure to distinguish L2 contrasts is originated from the divergence of perception and production betwixt L1 and L2 sound systems (All-time 1995; Flege 1995). In spite of these bug, a few studies observed L2 learners' successful perception and production of new L2 contrasts regardless if the new contrasts are involved in their native sound inventory or not (Flege and Hillenbrand 1984; Bohn and Flege 1990; Jun and Cowie 1994). More than prior studies have stated negative opinions near setting up a divide L2 phonetic subsystem that departs from L1 sound organization. Instead of accepting the existence of carve up audio systems in L2 learners, they rather argued a mutual influence between L1 and L2 phonetic systems sharing 'common' sound category (Flege 1995, 1999). Flege (1995, 1999) argued not only for the being of 'common space' between L1 and L2 sound systems but also that bilinguals' native phonetic category does non remain static merely it undergoes continuous modification and reorganization by reflecting new L2 sounds.
Ii dominant models of cross-language vowel perception (i.eastward., the Perceptual Assimilation Model (PAM) (Best 1995) and the Speech Learning Model (SLM) (Flege 1995) are originated from the consideration of how the strange vowels are assimilated to native phoneme categories. The idea of a perceptual equivalence class to account for the significant effect that some non-native vowels are more readily accommodated than others by 2d language learners was proposed by Flege (1987). Certain L2 sounds are sufficiently phonetically dissimilar from their nearest L1 targets to be perceived as "new" or "foreign", whereas others are sufficiently close to L1 targets to exist classified every bit "similar", though non identical to some L1 phonemic target. Afterward, Flege and Munro (1994) proposed that phonetic distance between vowels could be related directly to distances betwixt bespeak targets in the Bark-scaled F1 -f 0 / F 2 -F1 plane (Syrdal and Gopal 1986).
Both the Perceptual Absorption Model and the Speech Learning Model assumed that incorrect perceptions of L2 phones by adult L2 speakers are due to the assimilation of L2 phones to L1 categories, and this assimilation tin be featured on the ground of L2 speakers' linguistic background. All-time (1995) and Flege (1992, 1995) proposed that some non-native speakers' difficulty in the perception and product of L2 sounds may event from perceptual absorption of both L1 and L2 sound systems. According to Best's (1995) Perceptual Assimilation Model, non-native speakers' perception relies on their native phonemic systems, thus, if a certain phoneme from the L2 is perceptually alloyed to their L1 system, this audio is successively perceived by non-native speakers. However, if an L2 sound is hard to assimilate to the L1 category, non-native speakers will have trouble contrasting this audio from their native phonemic category. Best (1995) suggested two different types of assimilations. The first assimilation blazon is the assimilation of Unmarried Category (SC) which deals with 'new' L2 phone'southward assimilation to a single L1 category. The 2nd type is the absorption of Two Category (TC) which shows the being of 'similar' L2 contrasts with counterparts in L1 system.
Studies on Korean acquisition of L2 vowel system are notwithstanding rare. Ingram and Park (1997) examined the perception and production of Australian English language monophthongal non-back vowels:(/ i, ɪ, e, æ, a:/) by native speakers of Korean and Japanese, at two levels of English language experience. They also examined prototypicality ratings, or perceived similarities of the foreign vowels to their nearest native (L1) phonemic targets, to evaluate models of cross-linguistic communication vowel perception. Their report was the first reported instance of how a phonemic merger in Korean (vowels /ɛ/ and /e/), resulting in cross-generation differences within a speech communication community, can influence speakers' perception and product of non-native vowels. The furnishings of L1 phonological learning on vowel perception were also observed in the tendency of the Japanese, only non the Korean listeners, to normalize tokens of non-native vowels for speaker-dependent durational variation, consistent with the respective phonological roles of vowel length in Japanese and Korean. In another study, Baker and Trofimovich (2005) examined /i, ɪ, u, ʊ, e, ɛ/ English vowel productions past Korean-English bilinguals and the Korean and English monolinguals. The vowel production of Korean-English language bilinguals was so compared with each of the Korean and English monolinguals' vowel product. This comparison allowed them to examine how Korean-English language bilinguals' vowel production differs from each of the Korean and English monolinguals' and the result showed the difference of a caste and the direction of L1-L2 interaction between late vs early on bilinguals. They plant a unidirectional influence of L1 on L2 from late bilinguals' vowel production, but from early bilinguals' vowel production, a bidirectional L1 and L2 influence was observed. It seems that tardily bilinguals tended to rely by and large on their L1 sound category in the procedure of L2 production, however, early bilinguals seem to institute a new sound category for L2 contrasts distinct from their L1, which helps the early bilinguals perform more practiced L2 product. Based on their findings, Bakery and Trofimovich (2005) came to a conclusion that the amount of L2 experience influences the L1 and L2 human relationship and its influence between L1 and L2 is observed more than prominently among early on bilinguals than late bilinguals. Although the belatedly bilinguals have a certain corporeality of L2 experience, their L2 experience plays very piffling of a office in L2 acquisition. However, early bilinguals' L2 feel helps to perceive L1 and L2 phones as distinct phonetic property. L2 learners' historic period plays a substantial role in the relationship between L2 experience and a successful L2 acquisition. Before age of L2 acquisition shows a better effect on L2 acquisition than a later age of L2 learning.
In a contempo written report, Jung (2016) addressed Korean adult L2 learners' developmental English vowel acquisition process by demonstrating how adult L2 learners turn their initial L2 proficiency into more advanced land, and how new L2 sound system relates with existing L1 sound system. The report hypothesized that L2 learners' phonetic category is subject to modify followed by three stages of L2 vowel acquisition process: Stage 1 (Initial L2 proficiency), Phase ii (Intermediate L2 proficiency), and Stage iii (Avant-garde L2 proficiency). The study also hypothesized that L2 learners' identity /attitudes/motivation may have an influence on their L2 perception and product. The study carried out longitudinal experiments with 8 Korean adult L2 learners for 6 months. The experiments were conducted on a monthly footing and the procedure was controlled in a laboratory setting to examine whatsoever possible changes of L2 ability during L2 learning procedure. English language tense/lax vowel contrasts (/i/−/I/ and /u/−/(n/a)/) and Korean rounded/unrounded vowels (/(n/a)(i)/ and /(n/a)(u)/) were used for the experiments. The results demonstrated that Korean L2 learners' English vowel productions take changed to a more native-similar English vowel production through their L2 learning process. Thus, in the final experiment, Korean L2 learners' English vowel product showed almost an verbal similarity to native speakers' vowel production. The study too investigated the human relationship between adult L2 learners' identity/motivation/attitudes and their L2 vowel perception and production. The result indicated that higher identity/attitudes/motivation may event in avant-garde L2 vowel perception and product. L2 learners' L2 proficiency adult gradually. Hence the L2 learners' L2 learning is able to be considered to be following the sequential development design accompanied by the process of L2 learning.
Studies on the acquisition of Vietnamese vowels as an L2 are even rarer. Winn et al. (2008) investigated Vietnamese monophthong vowel product by native and American adult learners. Their results suggest that American adult learners struggled to produce the opposition between the cardinal /ɯ/ and back vowel /u/. The learners showed an insufficient advancement separation of these vowels every bit compared to native speakers.
In this newspaper, we nowadays new data and results on the role of prior L1 phonological and phonetic learning on the integration of vowel quality features in the production of L2 vowels. Specifically, this written report investigates adult L2 Korean learners' production of Vietnamese monophthong vowels. The findings of this written report will have an original and meaning contribution to the literature considering first, it presents a novel comparison: the acquisition of Vietnamese as an L2 is still understudied. Second, it contributes to the understanding of the process and nature of second linguistic communication conquering.
Vietnamese and Korean vowels
The Vietnamese vowel system contains nine long vowels, 2 curt vowels and 3 diphthongs. The long vowels are / i, ɛ, e, a, ɤ, o, ɔ, u, ɯ /; brusk vowels are / ɐ ʌ /; diphthongs are /ie, ɯɤ, uo/ (Dinh and Nguyen 1998). The Vietnamese vowel system has been described differently by dissimilar researchers: as a 9-vowel system (Nguyễn 1949, 1959; Haudricourt 1952; Đoàn 1977; Kirby 2011), equally a 10-vowel organisation (Smalley and Nguyen 1957, Le 1960, Crothers 1978), as an 11-vowel organisation (Thompson 1965, Han 1968), or every bit a xiv-vowel system with three diphthongs /ie/, /ɯɤ/ and /uo/ grouped with the monophthongs (Emerich 2012). The 9-vowel arrangement analysis lists these vowels /i e ɛ a ɔ o u ɤ ɯ/ as phonemes and the vowels /ɐ ʌ/ as allophones of phonemes /a ɤ/. These 9 vowels can occur in both open and airtight syllables, while the vowels /ɐ ʌ/ only occur in closed syllables. In this written report, nosotros examined 9 monophthongs /i due east ɛ a ɔ o u ɤ ɯ/ in open up syllables only. The 9 vowels of Vietnamese nether investigation in terms of tongue raising and advocacy are shown in Table 1, each phonetic symbol is followed by its equivalent letters in parentheses:
The number of monophthong phonemes of Seoul Korean varies, depending on scholars, from seven (i.e., /i, e, a, ʌ, o, u, ɨ /) to ten (plus /ɛ, ø, y/). Traditional researchers (Huh 1952, 1991; Lee 1996; Sohn 1999; Yang 1996, among others) consistently presented ten monophthongs as phonemes, probably due to the influence of the Korean writing system (Hangeul), which uses different graphemes for all those ten vowels. More recent phoneticians (Shin 2000; Hwang and Moon 2005) accept argued for a reduced number of vowels (7 to 9, instead of ten) based on acoustic phonetic research. The three front vowels /ɛ, ø, y/ are categorized differently by unlike researchers. In this study, we will exclude the two front rounded vowels /ø/ and /y/ as they are regarded equally diphthongs (/we/ and /wi/, respectively) by virtually researchers. Another disagreement is about the proper treatment of non-high unrounded vowels /east/ and the mid depression (or sometimes depression) vowel /ɛ/. However, it has repeatedly been observed that these two vowels are oftentimes realized identically or merged (Shin et al. 2013; Chung et al. 1988 and Umeda 1995). In addition, Korean is traditionally described equally possessing phonologically brusque and long vowels. Nonetheless, the length contrast seems to be disappearing in the Seoul dialect; it is preserved only in the speech of older speakers and just in the near formal speech style (commendation forms) (Ingram and Park 1997). In this paper, following Yoon et al. (2015), nosotros will investigate eight Korean vowels (namely / i, ɛ, e, a, o, u, ʌ, ɨ /).
Written report aims and plans
The aim of this report is to investigate the office of prior L1 phonological and phonetic learning on the integration of vowel quality features in the product of L2 vowels by examining adult L2 Korean learners' production of Vietnamese monophthongs in an imitation and a read aloud tasks. The study aims to accost three research questions:
- 1)
To what extent do Vietnamese and Korean vowels, as spoken by developed Vietnamese and Korean, differ or overlap in the acoustic phonetic infinite?
- two)
Are the phonetic features of L1 Korean vowels transferred to L2 Vietnamese and how Korean learners accommodate to the target Vietnamese vowel systems?
- 3)
How would the amount of similarity between Korean L1 and Vietnamese L2 sounds make up one's mind the degree of L1-L2 interaction in late bilinguals?
The program of this paper is as follows. First, Vietnamese and Korean speakers were asked to produce 9 Vietnamese and viii Korean vowels, respectively. These productions were then compared to decide the degree of cross-language similarity (or "overlap") betwixt Vietnamese and Korean vowels. The objective was to determine the extent to which Vietnamese and Korean vowels, equally spoken by adult Vietnamese and Korean, overlap in the audio-visual phonetic space. Next, these Vietnamese and Korean vowels were acoustically analysed to examine the caste of cross-language similarity between them. Based on these findings, predictions of how Korean learners would organize their phonetic organization(due south) were made. In the second part, adult Korean learners of Vietnamese were asked to produce the same Vietnamese vowels in two tasks: an faux and a read aloud task. These productions were then compared to those of Vietnamese and Korean speakers in part 1 to see whether the phonetic features of their L1 Korean vowels are transferred to Vietnamese, how they accommodate to the target Vietnamese vowel systems and how the amount of similarity betwixt Korean L1 and Vietnamese L2 sounds would decide the degree of L1-L2 interaction in late bilinguals.
Method
Participants
Three groups of participants took office in the study. A 'snowball' technique and stratified random sampling methods (Wiersma 2000) were used to find suitable participants through the first researcher's colleagues, students, friends, and friends of friends (participants were asked if they could recommend other people who would be interested in the experiments). In the 'snowball' technique, participants were selected by a combination of snowball sampling (where i contact leads to introductions to farther potential participants) and stratified random sampling, where the diverse categories of subjects are allocated to boxes (e.yard. local resident, male) and the boxes are progressively augmented until the desired cohort of subjects has been achieved. In the present case the iii boxes were: a command group of Northern Vietnamese (Hanoi), a control group of Korean speakers of Busan dialect, and native Korean L2 learners of Vietnamese from Busan University of Foreign Studies in South korea. The Vietnamese subjects tin exist said to represent Northern Vietnamese (Hanoi) speakers, the command group of Korean subjects represent Korean speakers of Busan dialect, and the Korean students represent Korean L2 learners of Vietnamese.
The control group of 11 Northern Vietnamese (Hanoi) speakers (6 females, five males) were international students at Macquarie Academy and have lived in Australia from half-dozen months to 1 year. Their average historic period was 35.3 (standard deviation (SD) = 7.two).
The command group of 10 Korean speakers (five females, v males) were international students of the Vietnamese studies program at the University of Social Sciences and Humanities, National Vietnamese University of Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. They all came from Busan, Southward Korea and have lived in Vietnam for 6 months. Their average age was 21 (SD = 1.iv).
The L2 learners of Vietnamese consisted of 11 native Korean speakers (5 males, 6 females) recruited from second-year students of Vietnamese Department of the Busan University of Foreign Studies in South Korea. Their average age was 21 years erstwhile (SD = ane.five) and their boilerplate length of learning Vietnamese was more than ane year (mean = 13.6 months). In the outset ii years of the four-year bachelor plan in Vietnamese studies, Korean students basically learn linguistic communication skills such as grammer, listening, speaking, reading and writing. In the terminal 2 years, they both learn the advanced linguistic communication skills and the Vietnamese specialised subjects such as Vietnamese civilisation, Vietnamese-Korean translation and interpretation, Vietnamese via media, Vietnamese via journalism, Vietnamese history, Vietnamese literature, Vietnamese politics, etc. Since these Korean speakers had studied Vietnamese in Republic of korea, they had little experience interacting with native Vietnamese speakers in native- environment contexts. Considering the Korean leaners started learning Vietnamese at the average age of 19.5 years, they tin exist considered as late learners of L2. Also, since they were merely 2d-year students from a four-year available plan in Vietnamese, their level of Vietnamese can be considered as pre-intermediate level.
Stimuli
The experiment used open syllables with the initial stop consonant /t−/ and the nine Vietnamese vowels /i/, /e/, /ɛ/, /ɯ/, /ɤ/, /a/, /u/, /o/, /ɔ /. These vowels were and then embedded in /t_/ carrier words. Each discussion independently carried one of the 6 Northern Vietnamese tones (run across Table 2). The total number of items included: (9 simple vowels × 6 tones, totalling 54 items). The syllables used in the report are all "legal" syllables, most of which were familiar to the participants.
Since the Korean learners learnt Vietnamese with instructors of Northern (Hanoi) dialect, ane male native speaker of Hanoi Vietnamese produced all the stimuli for the Imitation task, which were recorded at 44.i kHz using the born microphone of a laptop and the Praat software (Boersma and Weenink 2017). The stimuli were randomized in i cake with the inter-stimulus interval of 6 s. The total elapsing of the block is 13 min. The aforementioned stimuli were presented in written form via Powerpoint slides for the Read-Aloud task.
Each of the eight Korean vowels occurred in an / h(5)da / context. In Korean that is a typical course. For case, each verb stem combines with the particle da or h (V) da to form a root infinitive. The 8 Standard Korean vowels investigated were / i, ɛ, e, a, o, u, ʌ, ɨ /), every bit in hida, hɛda, heda, hada, hoda, huda, hʌda and hɨda. The chosen Korean words were disyllabic because it was impossible to find monosyllabic Korean words that had the same characteristics equally the Vietnamese stimuli. Nevertheless, this difference in syllable length across the word sets in the two languages was non seen to exist a limitation in comparing vowel quality in Vietnamese and Korean (see Yang 1996 and Baker and Trofimovich 2005 for an example of English and Korean vowel comparisons using monosyllabic English and disyllabic Korean word stimuli).
Procedures
Read-aloud chore
The control Vietnamese participants and L2 Korean learners of Vietnamese were asked to read aloud the 54 stimuli presented on Powerpoint slides (one word for each slide) at their ain pace. The order of the stimuli was randomized in a unlike order from the other task. Their responses were recorded past the Praat program on a laptop figurer.
Similarly, the control Korean speakers read the 8 disyllabic words containing viii Korean vowels five times each which were all later used in the analysis. Their responses were recorded by the Praat plan on a laptop computer. Information technology is noted that the words in Vietnamese and Korean were elicited in citation forms and the aforementioned microphone and laptop used for all recordings.
Imitation task
Only the L2 learners of Vietnamese participated in this task. The participants listened to each stimulus one time through headphones and were asked to repeat after it without any visual aid. Their responses were recorded by the Praat program on a laptop computer. They completed fake task before the Read-Aloud task.
Assessing accuracy in the read-aloud and imitation tasks
The recordings were judged by two phonetically trained native speakers of Vietnamese, who further identified the vowel errors fabricated by the participants. The two native speakers evaluated the recordings and labelled the vowel of each syllable/discussion with a choice among the nine Vietnamese vowels or the symbol x. That is, if a vowel is perceived equally not similar to any of the Vietnamese vowels, the vowel is labelled x. When at that place was any disagreement between them, the item was discarded. The two native judges agreed on most of the tokens (inter-rater understanding was 89% for the Fake task and 80% for the Read-Aloud task), and their divergence appeared to reverberate ambivalence in the productions. The learners' mean percentage accuracy and error rates for the nine Vietnamese vowels in the two tasks were calculated and summarized in confusion matrices, which are provided in Table 4. The final number of vowel judgement used in subsequent analysis were sufficient for reliable statistical analysis.
Data analysis
Acoustic analyses of the Vietnamese and Korean words were performed to make up one's mind: (1) how like (or different) the ix Vietnamese and viii Korean vowels were across the two languages, and (2) how like (or dissimilar) the Korean learners' nine Vietnamese vowels were from the target L2 Vietnamese and their L1 Korean.
Acoustic analyses of Vietnamese and Korean vowels were express to the fundamental frequency (F0) too equally the start two vowel formants (F1, F2). Although it is possible that the two languages may differ significantly in other dimensions of vowel acoustics (e.thou., vowel duration or diphthongization) and that Korean learners may exploit these differences to brand distinctions across their two languages, analyses of these vowel properties were not possible within the present study considering of the differences in syllable length across the word sets in the ii languages. More specifically, the vowels were analysed by measuring fundamental frequency (F0) likewise equally the first two vowel formants (F1, F2) at vowel midpoint. The vowels were measured using the get pitch and formant listing commands from the Praat program (Boersma and Weenink 2017).
The vowel-formant values (in Hz) were and then converted to Bark scale (B) to normalize for gender and age differences in vowel production (Syrdal and Gopal 1986) by using the formula: B = 26.81 / (1 + (1960 / F)) − 0.53. Two other measures were derived from the obtained vowel-formant values: B1-B0 (B1 minus B0) and B2-B1 (B2 minus B1). B1-B0 is an gauge of vowel position in the high-low dimension, where lower values represent high vowels and higher values represent low vowels. B2-B1 is an estimate of vowel position in the front-back dimension, where lower values represent back vowels and higher values correspond front vowels. The vowels were and then plotted in the audio-visual infinite with B2-B1 values on the X-axis and B1-B0 values on the Y-axis and results were presented in Figs. 1, ii, 3, 4 and 5.
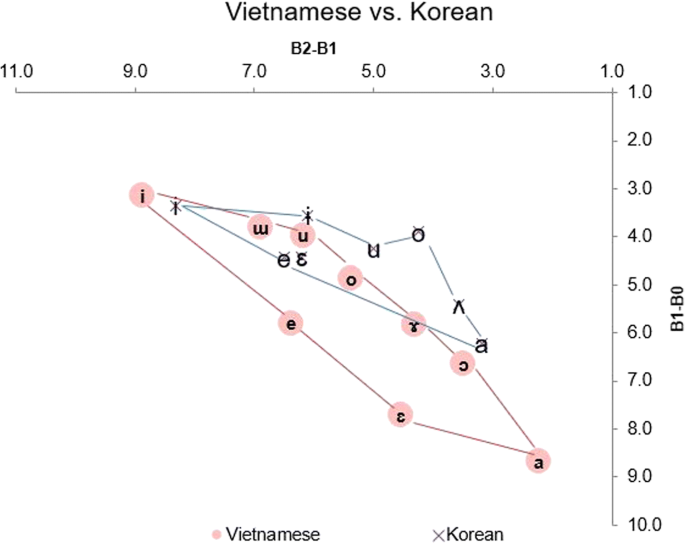
Cantankerous-language comparison of vowels produced by the command Vietnamese and control Korean speakers. X-axis: B2-B1(Bark): vowel frontedness, y-axis: B1-B0(Bark): vowel height
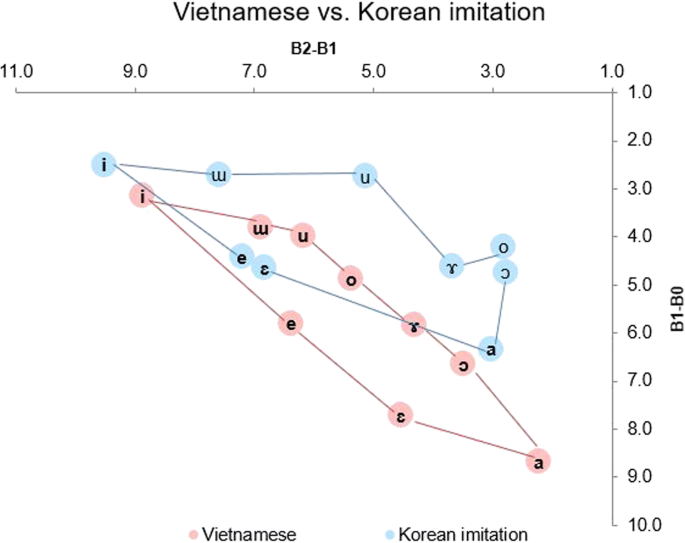
Vietnamese vowels produced past Korean learners in the imitation task and control Vietnamese. X-axis: B2-B1(Bark): vowel frontedness, y-centrality: B1-B0(Bawl): vowel elevation

Vietnamese vowels produced by Korean learners in the read aloud task and control Vietnamese. X-centrality: B2-B1(Bawl): vowel frontedness, y-centrality: B1-B0(Bark): vowel superlative
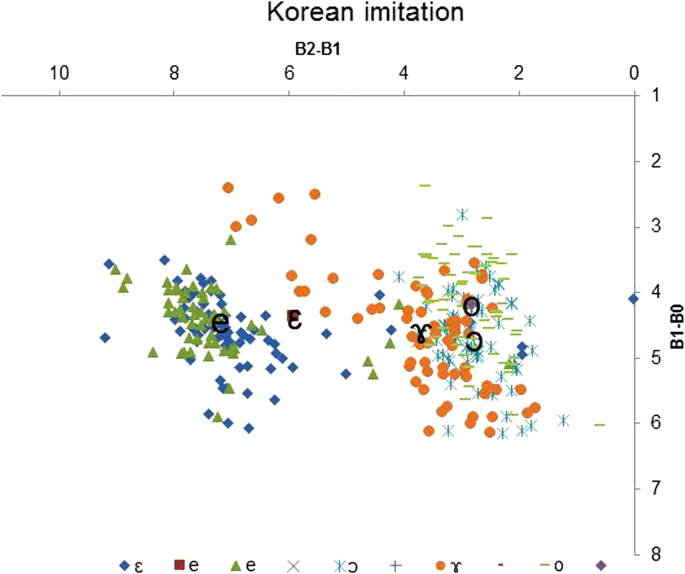
The merging patterns of Vietnamese vowels produced by Korean learners in the imitation task. Ten-axis: B2-B1(Bark): vowel frontedness, y-axis: B1-B0(Bark): vowel peak
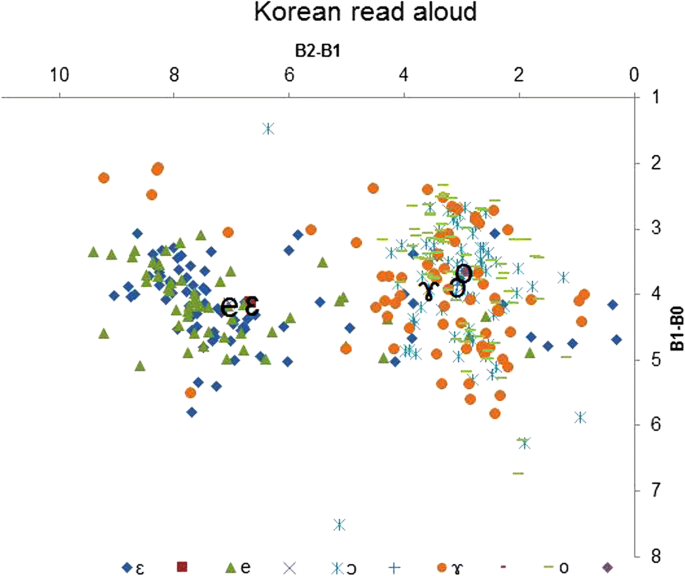
The merging patterns of Vietnamese vowels produced by Korean learners in the read-aloud task. X-axis: B2-B1(Bark): vowel frontedness, y-axis: B1-B0(Bark): vowel height
Statistical analysis
Start, in gild to respond the starting time research question, cross-language comparisons of vowels produced by the control Vietnamese and control Korean speakers were carried out within each of the vowel sets (Vietnamese /a/-Korean /a/, Vietnamese / ɛ/-Korean / ɛ/, Vietnamese /eastward/-Korean /due east/, Vietnamese /i/-Korean /i/, Vietnamese / ɔ/-Korean/o/, Vietnamese/o/-Korean/o/, Vietnamese/ ɤ/-Korean/ʌ/, Vietnamese/u/-Korean/u/, and Vietnamese /ɯ/-Korean/ ɨ/. In order to account for the effect of speakers' differences and the intrinsic segmental and tonal furnishings, a restricted maximum likelihood (REML) practical to mixed model methodology was performed on the vowel acme (B1-B0) and vowel frontedness (B2-B1) values. The fixed upshot included groups (four groups: Korean, Korean imitation, Korean read aloud and Vietnamese). The random effect was speakers (32 speakers: 11 control Vietnamese, eleven Korean learners, and 10 control Korean speakers). The use of REML overcomes the potentially serious deficiency of the ANOVA-based methods which assumed that data are sampled from a random population and normally distributed. REML also avoids bias arising from maximum likelihood estimators in which all fixed furnishings are known without errors, consequently tend to downwardly bias estimates of variance components. Moreover, REML tin handle unbalanced data. The data analysis was carried out using the SPSS program. The results are reported in Table three.
Second, in order to answer the 2nd and third inquiry questions, comparisons of vowel pairs, which take potential to overlap or merge, within each speaker groups (control Vietnamese, control Korean, Korean Imitation and Korean read aloud) were carried out inside each of the iii vowel sets (/ ɛ/−/e/, / ɔ/−/o/−/ ɤ/, and /u/−/ ɯ/). The fixed effect was vowels. The random result was speakers. A Tukey post-hoc test was then conducted to decide the significant differences amongst the levels of the main furnishings. The results are presented in Table 5 in Appendix.
Results
Vietnamese and Korean cross-linguistic communication comparisons of vowels
The mixed effect modals showed pregnant effects for the main factor groups for all vowel pairs (F (3,332) =3.0–sixty.4, p < 0.05–0.0001). As shown in Fig. one and Table 3, Vietnamese and Korean vowels differ significantly in terms of vowel height (B1-B0, p < 0.02–0.001) for vowels /a/, / ɛ/, /e/, / ɔ/, /o/ and / ɯ/. By contrast, there are some overlapping of vowel height betwixt the ii languages, specifically betwixt vowels such as Vietnamese /i/ and Korean/i/: p = 0.66 ns., Vietnamese / ɤ/ and Korean /ʌ/: p = 0.25 ns., Vietnamese /u/ and Korean /u/: p = 0.three ns. In addition, in that location are also some overlapping of vowel frontedness between the 2 languages, peculiarly Vietnamese /east/-Korean /eastward/: p = 0.67 ns., Vietnamese /i/ and Korean/i/: p = 0.55 ns., Vietnamese /ɤ/ vs. Korean /ʌ/: p = 0.07 ns., and Vietnamese /ɯ/ vs. Korean / /ɨ/: p = 0.06 ns. Particularly, information technology is shown by Fig. 1 that Korean vowels / ɛ/ and /e/ merged across all speakers. In addition, Korean /ʌ/ is shown to be in proximity with Vietnamese / ɔ / and /ɤ/. Therefore, information technology is predicted that Korean L2 speakers of Vietnamese will have difficulty distinguishing the Vietnamese vowels / ɛ/ and /east/. Furthermore, it is expected that they will have issues discriminating Vietnamese vowels /ɔ/, /o/ and /ɤ/ in their production. By contrast, it is likewise predicted that they can produce acoustic differences for those L1-L2 vowels pairs that were highly dissimilar, such equally /a/ (p < 0.001).
Vowel error patterns in read-aloud and imitation tasks
As shown in Tabular array 4, Korean learners produced significantly more Vietnamese-similar vowels in the fake task than in the read aloud task. This is indicated in the result of an ANOVA analysis with a significant effect for tasks (p < 0.0001). This is also shown in the pct of symbol 10 used: but half-dozen.06% (36/594 items) of the items in the false task were identified by the 2 researchers equally not sounding similar to any Vietnamese vowels. By contrast, in the read aloud task, 23.74% (141/594 items) were identified as x. This result suggests that Korean leaners accommodate to the native Vietnamese speaker to a greater extent in an imitation than in the read aloud chore.
In the imitation task, there are two main mistake patterns: Korean learners accept problems distinguishing Vietnamese vowel pairs / ɛ/−/eastward/ and /o/−/ɔ/ in their production. Korean learners tend to produce Vietnamese vowel / ɛ/ as /e/ (17%) while they have no problem imitating Vietnamese vowel /east/. Similarly, they tend to produce vowel /ɔ/ as /o/ (33%). In the read aloud chore, they as well have difficulty producing the vowel /ɛ/ (i.due east., /ɛ/ pronounced every bit /e/: ix% and non-native similar: 68%). They also could not distinguish betwixt /o/ and /ɔ/, /o/ and/ ɤ/, and /u/ and /ɯ/. These error patterns back up the predictions in "Vietnamese and Korean cross-language comparisons of vowels" section.
Acoustic comparison of Vietnamese vowels produced by Korean learners and control Vietnamese
As shown in Figs. 2 and 3, Korean learners produced vowels which have significantly higher vowel pinnacle than those of control Vietnamese speakers across both tasks: imitation and read aloud. This mirror the pattern found in "Vietnamese and Korean cross-language comparisons of vowels" section: vowels of control Korean speakers besides have higher vowel height than that of control Vietnamese.
In addition, Vietnamese vowels /ɛ/ and /eastward/ produced by Korean learners merged in vowel space, supported by the statistical analysis equally reported in Tabular array 5 in Appendix and Figs. 4 and 5. This is consequent with the acoustic results in "Vietnamese and Korean cross-linguistic communication comparisons of vowels" section and perception results by ii phoneticians in "Vowel error patterns in read-aloud and imitation tasks" section. The statistical issue in Tabular array iii besides shows that in that location was no meaning difference betwixt Korean learners (KI and KR) and command Korean speakers (K) in terms of vowel /e/ and /ɛ/ (the bolded results in Table three), suggesting that the Korean learners digest their L2 Vietnamese vowels to their L1 Korean vowel.
Moreover, the three Vietnamese vowels /ɔ/, /o/ and/ ɤ/ produced past Korean learners in both tasks tend to cluster together. This is also supported by the statistical analysis in Table five in Appendix and Figs. 4 and 5. Specifically, there was no significant difference in vowel superlative of vowels /ɔ/−/ɤ/ and the vowel frontedness of the vowels /ɔ/−/o/ overlapped for both tasks (imitation and read aloud).
The statistical effect (Table 5 in Appendix) indicates that Korean vowel pair /u/−/ɨ/ has equivalent height (B1-B0: p = 0.44 ns.). In contrast, Korean learners' (KI and KR) Vietnamese vowels /u/−/ɯ/ are of the same vowel height (B1-B0: p = 0.78 ns. and p = 0.63 ns., respectively).
Discussion
In this section, we summarize and discuss the results by addressing the three research questions raised in "Written report aims and plans" department.
Starting time, to what extent do Vietnamese and Korean vowels, as spoken past adult Vietnamese and Korean, differ or overlap in the audio-visual phonetic infinite?
The result on cantankerous language comparison showed that Vietnamese and Korean vowels differ significantly in terms of vowel meridian. By contrast, there are some overlapping of vowel frontedness between the two languages (peculiarly Vietnamese /e/-Korean /e/, Vietnamese /i/ and Korean/i/, Vietnamese /ɤ/ vs. Korean /ʌ/, and Vietnamese /ɯ/ vs. Korean / /ɨ/). In addition, Korean vowels /ɛ/ and /e/ were institute to merge across all speakers. This is consistent with previous studies (Shin et al. 2013; Chung et al. 1988 and Umeda 1995). Furthermore, Korean /ʌ/ is shown to exist in proximity with Vietnamese / ɔ/ and /ɤ/. By contrast, in that location were acoustic differences for those L1-L2 vowel pairs that were highly dissimilar, such equally Vietnamese /a/ and Korean /a/.
2nd, are the phonetic features of L1 Korean vowels transferred to L2 Vietnamese and how Korean learners adjust to the target Vietnamese vowel systems?
The merging of / ɛ/ and /e/ in Korean is transferred into Vietnamese, leading Korean learners to inability to distinguish the target language vowel dissimilarity / ɛ/ and /e/ in production. This shows that an on-going phonemic merger in L1 can differentially bear upon upon learners' false and product of a similar vowel contrast in L2, consistent with findings on Korean learners' conquering of English language vowels in a previous study (Ingram and Park 1997). This could exist predicted from any of the models of cross-linguistic communication vowel perception (due east.g., Flege 1995; Best 1995). It seems nearly likely that the L2 perception and production differences were expressions of L1 perceptual learning effects. In other words, wrong perception of L2 phones by adult learners is considered to exist due to the absorption of L2 phones to L1 categories. This can exist explained according to Best (1995) model: the Korean learners may have assimilated Vietnamese vowel / ɛ/ and /e/ contrast to a unmarried Korean /e/ category since there is no such counterpart of vowel / ɛ/ in Korean vowel arrangement due to the merger, and which shows the example of Single Category type. The same principle applies to the Vietnamese /o/ and /ɔ/ contrast, Korean has /o/ but non /ɔ/, thus they tend to pronounce Vietnamese /ɔ/ as /o/, suggesting that they assimilated Vietnamese /o/ and /ɔ/ to a unmarried Korean /o/.
Furthermore, the three Vietnamese vowels /ɔ/, /o/ and/ ɤ/ produced by Korean learners in both tasks tend to cluster together. This may be due to the promixity in acoustic space of the Korean vowels /o/ and /ʌ/ to the Vietnamese vowels /ɔ/, /o/ and/ ɤ/. This provided insights into how cross-language similarity influenced the L1-L2 interaction. That is, when Vietnamese and Korean vowels were relatively like acoustically, the Korean learners' renditions of L2 (Vietnamese) vowels were strongly "colored" by the acoustic properties of their L1 (Korean) vowels, consistent with findings by Trofimovich and Baker (2006) on Korean speakers of English.
In addition, the result on L2 vowel production also indicates that Korean learners' Vietnamese vowels are higher than those of the control Vietnamese, suggesting that Korean leaners tend to transfer their L1 vowel acoustic space into the production of Vietnamese vowels.
Third, how would the corporeality of similarity between Korean L1 and Vietnamese L2 sounds decide the degree of L1-L2 interaction in late bilinguals?
The results of this report indicated that cross-language similarity indeed influenced how the L2 vowels are produced. That is, vowels that were highly similar across the two languages were more than likely to influence each other (such as / ɛ/ and /e/) than those vowels that were dissimilar (such equally /a/). The late bilinguals in this report produced acoustic differences only for those L1-L2 vowel pairs that were highly dissimilar, such equally Vietnamese /a/ and Korean/a/. Assuming that L1-L2 interaction implies restructuring of the L1 and L2 phonetic system(s), then the degree of acoustic similarity between L1 and L2 sounds constrains what sounds undergo such a restructuring and the degree to which it does so (Trofimovich et al. 2001). The interaction hypothesis (Flege et al. 1995) may explain why cross-linguistic communication similarity is more likely to determine how adult L2 learners organize their phonetic organisation(s). Considering late bilinguals' L1 categories are fully developed, they are more probable to produce even perceptually unlike L1 and L2 sounds with L1-based acoustic properties (Aoyama et al. 2004) and to perceive such L2 sounds in terms of an L1-based category (Guion et al. 2000; Trofimovich et al. 2001). The tardily bilinguals in this study may require an corporeality of experience with the L2 that is far greater than that explored in this study (more than one twelvemonth) in order to overcome the pervasive effect of their L1 on their processing and learning of L2 sounds (Flege et al. 1995; Trofimovich et al. 2001).
Additionally, the effect of the report also implies the effect of Korean learners' vowel perception on their production by means of the faux task. The fact that they failed to imitate the vowel pairs / ɛ/−/e/ and /o/−/ɔ/ accurately suggests that they have problems perceiving the vowel contrast in L2. Flege (1995) pointed to the importance of the human relationship between perception and production. He hypothesized that accurate perception of L2 sounds will eventually lead to the successful product of L2 phones. If an L2 learner shows difficulty in discriminating L2 contrasts, the learner would also have the same difficulty producing correct L2 phones in L2 learning. Further inquiry examining how cross-language similarity influences the perception of the L2 may indicate to what extent this power constrains both the perception and the production abilities of bilinguals.
Furthermore, Korean learners produced significantly more Vietnamese-like vowels in the simulated task than in the read aloud chore. This result suggests that Korean leaners accommodate to the native Vietnamese speaker to a greater extent in an imitation than in the read aloud task. This tin can be explained by the phonetic convergence effect which is divers every bit the procedure by which a talker takes on acoustic characteristics of the private that he or she is interacting with (Boom-boom 2012). The results revealed a significant convergence with the model in the chore in which speakers were required to immediately echo after the model voice (imitation chore) compared to the job in which they read orthographic representations of the words (read aloud task). Hence, it suggests that foreign language learners are able to change their productions of non-native vowels every bit a event of exposure to the model. The result that Korean learners get more similar in their product to the target language speaker in the simulated task would besides imply that fine-grained phonetic details are not filtered out in speech perception and detailed auditory traces associated with perceived words are stored in memory and are then used for production (Dufour and Nguyen 2013).
Finally, the result of this report is consistent with that of Bakery and Trofimovich (2005) who institute that late bilinguals tended to rely mostly on their L1 sound category in the process of L2 production, however, in their study, early bilinguals seem to establish a new sound category for L2 contrasts distinct from their L1, which helps the early on bilinguals perform more proficient L2 production. Although the tardily bilinguals in this study and in Baker and Trofimovich (2005)'s inquiry have a sure amount of L2 experience, their L2 experience plays very lilliputian of a part in L2 conquering. This showed that L2 learners' historic period plays a substantial role in the relationship between L2 feel and a successful L2 acquisition. In other words, earlier age of L2 acquisition shows a better effect on L2 acquisition than a later historic period of L2 learning. Therefore, the findings of this study are limited to developed's situation. Nevertheless, Jung (2016)'s study provided some evidence for the claim of developmental stages of L2 learning. In the 2d-Linguistic communication Linguistic Perception (L2LP) model, Escudero (2006) proposed a developmental procedure of L2 learning. The model suggested that a total copy of L1 audio occurs at the initial country of L2 learning, and through creating and adjusting L1 and L2 category, at the end country, avant-garde L2 learners brainstorm to separate the L1 and L2 sound arrangement. Escudero asserted that the existence of a separate sound category of L1 and L2 leads the learners to an optimal stage of L2 perception. The L2LP model also proposed that the key to L2 evolution is driven by rich L2 input such every bit qualified L2 instruction. L2 learners are able to benefit from L2 community environments likewise by acquiring disquisitional auditory cues from a target customs. Therefore, future studies should include additional Korean participants with intermediate or higher levels and with "richer L2 input and/or qualified L2 educational activity" that could reveal a diverseness of transfer issue and L2 development process.
Conclusion
In summary, this paper presents new data and results on the roles of linguistic communication-specific phonological learning and inherent phonetic contrastiveness in the production of non-native vowels. The results of this report provide show that Korean learners transfer their L1 vowel quality features into the production of Vietnamese vowels. The findings of this study have an original and pregnant contribution to the literature considering outset, it presents a novel comparison: the conquering of Vietnamese as an L2 is nonetheless understudied. 2nd, information technology contributes to the understanding of the process and nature of 2d language acquisition. While the results of this study are specific to Korean and Vietnamese, their implications can exist extended to the acquisition of other languages. In fact, a series of studies on speakers of other languages (e.g. Lao, Taiwanese and Japanese) learning Vietnamese as an L2 are being conducted by the authors.
Abbreviations
- B:
-
Bark
- B1-B0:
-
Vowel acme values
- B2-B1:
-
Vowel frontedness values
- F0:
-
Cardinal frequency
- F1:
-
Kickoff vowel formant
- F2:
-
2nd vowel formant
- K:
-
Command Korean
- KI:
-
Korean imitation
- KR:
-
Korean read aloud
- L1:
-
Native language
- L2:
-
Second linguistic communication
- L2LP:
-
Second-Language Linguistic Perception model
- PAM:
-
Perceptual Assimilation Model
- REML:
-
Restricted maximum likelihood
- SC:
-
Single Category
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SLM:
-
Speech Learning Model
- TC:
-
Ii Category
- V:
-
Control Vietnamese
References
-
Aoyama, Chiliad., Flege, J. Eastward., Guion, S. Thou., Akahane-Yamada, R., & Yamada, T. (2004). Perceived phonetic dissimilarity and L2 speech learning: The instance of Japanese /r/ and English /r/ and / l/. Journal of Phonetics, 23, 233–250.
-
Babel, M. (2012). Show for phonetic and social selectivity in spontaneous phonetic imitation. Journal of Phonetics, xl, 177–189.
-
Baker, W., & Trofimovich, P. (2005). Interaction of native- and second-language vowel organization(s) in early on and late bilinguals. Language & Voice communication, 48, ane–27.
-
All-time, C. T. (1995). A direct realist view of cross-linguistic communication speech perception. In W. Foreign (Ed.), Oral communication perception and linguistic experience: problems in cantankerous - linguistic communication research (pp. 171–203). Baltimore: York Press.
-
Boersma, P. & Weenink, D. (2017). Praat: doing phonetics by figurer (version 6.0.26). computer programme. Retrieved 1 January 2017, from http://world wide web.praat.org/ California, Los Angeles.
-
Bohn, O.-Due south., & Flege, J. (1990). InterIingual identification and the role of strange linguistic communication experience in L2 vowel perception. Practical PsychoLinguistics, 11, 303–328.
-
Brunelle, M. (2015).Vietnamese (Tiếng Việt). The handbook of Austroasiatic languages (pp. 909–954). Leiden: Brill.
-
Chung, H, Makino, S, & Kido, Grand (1988). Analysis and recognition of Korean isolated vowels using formant frequency. Journal of the Acoustic Social club of Nihon, 9(five), 225–232.
-
Crothers, J. (1978). Typology and universals of vowel systems. Universals of human language. In J. H. Greenberg (Ed.), Phonology (Vol. 2, pp. 95–152). Stanford: Stanford University Press.
-
Dinh, L. T., & Nguyen, V. H. (1998). Cơ cấu ngữ âm tiếng Việt [Construction of Vietnamese phonetics]. Thành phố Hồ Chí Minh: Giáo Dục Printing.
-
Đoàn, T. T. (1977). Ngữ âm tiếng Việt [Vietnamese phonetics] (pp. one–371). Nhà Xuất Bản Đại Học Quốc Gia: Hà Nội.
-
Dufour, S., & Nguyen, N. (2013). How much fake is there in a shadowing job? Frontiers in Psychology, 4, ane–7.
-
Emerich, Chiliad. H. (2012). The Vietnamese vowel system. Ph.D thesis. University of Pensylvania.
-
Escudero, P. (2006). The phonological and phonetic evolution of new vowel contrasts in Spanish learners of English. In B. Baptista & M. Watkins (Eds.), English language with a Latin beat out: studies in Portugues/Spanish-English language interphonology. Studies in bilingualism (Vol. 31, pp. 149–161). Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
-
Flege, J. (1999). The relation between L2 production and perception. In J. Ohala, Y. Hasegawa, Grand. Ohala, D. Granveille, & A. Bailey (Eds.), Proceedings of the XIVth International Congress of Phonetics Sciences (pp. 1273–1276). Berkeley: Department of Linguistics, Univ. of California at Berkeley.
-
Flege, J., & Hillenbrand, J. (1984). Limits on pronunciation accuracy in developed foreign linguistic communication speech production. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 76, 708–721.
-
Flege, J. E. (1987). The production of "new" and "similar" phones in a foreign linguistic communication: Evidence for the effect of equivalence nomenclature. Journal of Phonetics, fifteen, 47–65.
-
Flege, J. E. (1992). Talker and listener effects on caste of perceived foreign accent. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 91(one), 370–389.
-
Flege, J. E. (1995). 2nd language speech learning theory, findings, and problems. In W. Strange (Ed.), Speech perception and linguistic experience: issues in cross - language research (pp. 233–277). Baltimore: York Press.
-
Flege, J. E., & Munro, M. J. (1994). Auditory and chiselled effects on cross-language vowel perception. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 95(6), 3623–3641.
-
Flege, J. E., Munro, M. J., & MacKay, I. R. A. (1995). Factors affecting degree of perceived foreign accent in a second language. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 97, 3125–3134.
-
Guion, South., Flege, J., Akahane-Yamada, R., & Pruitt, J. (2000). An investigation of current models of second linguistic communication speech perception: The case of Japanese adults' perception of English consonants. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 107, 2711–2725.
-
Han, Chiliad. South. (1966). Vietnamese vowels. Studies in the phonology of Asian languages iv. Los Angeles: Acoustic Phonetics Enquiry Laboratory, University of Southern California.
-
Han, Yard. S. (1968). Circuitous syllable nuclei in Vietnamese. Studies in the phonology of Asian languages (vol. 6); U.Southward. Function of Naval Research. Los Angeles: Academy of Southern California.
-
Haudricourt, A. G. (1952). Les Voyelles brèves du vietnamien. Bulletin de la Société de Linguistique de Paris, 48(1), 90–93.
-
Huh, W. (1952). Ay, ey, oy, ɔ uy umka ("on the sound quality of ay, ey, oy, o, ɔ"). Kukeo Kukmunhak, 1, 5–8 (in Korean).
-
Huh, Westward. (1991). Korean phonology. Seoul: Sam Munhwasa (in Korean).
-
Hwang, H., & Moon, S. (2005). An acoustic comparative study of Korean /에, 애/ and English /ɛ, æ/ pronounced by Korean immature male speakers. Malsori, 56, 29–47 (in Korean).
-
Ingram, J. C., & Park, S.-M. (1997). Cross-language vowel perception and product past Japanese and Korean learners of English. Periodical of Phonetics, 25(3), 343–370.
-
Jun, S.-A., & Cowie, I. (1994). Interference for 'new' versus 'similar' vowels in Korean speakers of English. In Working papers in linguistics (Vol. 43, pp. 117–130). Dept. of Linguistics, The Ohio Country University.
-
Jung, J. E. (2016). A developmental procedure of English vowel acquisition by Korean adult L2 learners. Ph.D dissertation. Buffalo: State Academy of New York.
-
Kirby, J. P. (2011). Vietnamese (Hanoi Vietnamese). Journal of the International Phonetic Association, 41(three), 381–392.
-
Le, V. L. (1960). Le Parler Vietnamien (2nd ed.). Saigon: Bo Quoc Gia Giao Duc.
-
Lee, H. (1996). Korean phonetics. Seoul: Taehaksa (in Korean).
-
Nguyễn, B. T. (1949). Chữ và Vần Việt Nam Khoa Học [scientific study of Vietnamese letters and syllables]. Sài Gòn: Ngôn Ngữ.
-
Nguyễn, B. T. (1959). Ngôn Ngữ học Việt Nam [Vietnamese linguistics]. Sài Gòn: Ngôn Ngữ.
-
Nguyễn, Đ. H. (1997). Tiếng Việt Không Son Phấn [Vietnamese without veneer]. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
-
Shin, J. (2000). Understanding spoken communication. Seoul: Hankuk Munhwasa (in Korean).
-
Shin, J., Kiaer, J., & Cha, J. (2013). The sounds of Korean. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
-
Smalley, W. A., & Nguyen, V. V. (1957). Vietnamese for missionaries: a course in the spoken and written language of Central Viet Nam, I & II. Saigon.
-
Sohn, H. (1999). The Korean language. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press (in Korean).
-
Syrdal, A. K., & Gopal, H. S. (1986). A perceptual model of vowel recognition based on the auditory representation of American English language vowels. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 79, 1086–1100.
-
Thompson, Fifty. C. (1965). A Vietnamese reference grammar. Honolulu: Academy of Hawai'i Press.
-
Trofimovich, P., Bakery, W., & Mack, M. (2001). Context and experience-based effects on the learning of vowels in a second language. Studies in the Linguistic Sciences, 31(2), 167–186.
-
Trofimovich, P., & Bakery, West. (2006). Learning 2nd language suprasegmentals: Effect of L2 experience on prosody and fluency characteristics of L2 spoken communication. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 28, 1–30.
-
Umeda, H. (1995). Age differentiation of the vowel system in the Seoul Korean: Acoustic measurements. Journal of Asian and African Studies, 48-49, 443–453.
-
Wiersma, W. (2000). Research methods in education: an introduction. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
-
Winn, K., Blodgett, A., Bauman, J., Bowles, A., Charters, L., Rytting, A., & Shamoo, J. (2008). Vietnamese monophthong vowel production by native speakers and American adult learners. In Proceedings of acoustics '08 (pp. 6125–6130).
-
Yang, B. (1996). A comparative study of American English and Korean vowels produced by male and female speakers. Journal of Phonetics, 24, 245–261.
-
Yoon, T.-J., Kang, Y., Han, S., Maeng, H., Lee, J., & Kim, K. (2015). A corpus-based approach to dialectal variation in Korean vowels. In Proceedings of the 18th ICPhS.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the subjects for their voluntary participation in the experiment. Nosotros also give thanks the two anonymous reviewers for their effective comments.
Writer information
Affiliations
Contributions
M-DD collected the data. A-TTN conducted the acoustic and statistical analysis of the information and wrote the paper. Both authors designed the experiments, read and canonical the last manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ideals declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they accept no competing interests.
Publisher'southward Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed nether the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution four.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/past/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you requite appropriate credit to the original author(south) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and signal if changes were made.
Reprints and Permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Đào, Đ.Thou., Nguyễn, AT.T. L1 Korean vocalic transfer in adult L2 Korean learners' product of Vietnamese monophthong vowels. Asian. J. 2nd. Strange. Lang. Educ. 3, 13 (2018). https://doi.org/x.1186/s40862-018-0055-one
-
Received:
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
DOI : https://doi.org/x.1186/s40862-018-0055-1
Keywords
- Vowels
- Korean
- Vietnamese
- Second language conquering
- Audio-visual phonetics
Source: https://sfleducation.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40862-018-0055-1
0 Response to "Long and Short Vowels in Korean Peer Reviewed Articles"
Post a Comment